APOD: Milky Way Auroral Flower (2022 Oct 18)
Posted: Tue Oct 18, 2022 4:09 am
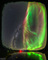 Milky Way Auroral Flower
Milky Way Auroral FlowerExplanation: Could the stem of our Milky Way bloom into an auroral flower? No, not really, even though it may appear that way in todayâs featured all-sky image. On the left, the central plane of our home galaxy extends from the horizon past the middle of the sky. On the right, an auroral oval also extends from the sky's center -- but is dominated by bright green-glowing oxygen. The two are not physically connected, because the aurora is relatively nearby, with the higher red parts occurring in Earth's atmosphere only about 1000 kilometers high. In contrast, an average distance to the stars and nebulas we see in the Milky Way more like 1000 light-years away - 10 trillion times further. The featured image composite was taken in early October across a small lake in Abisko, northern Sweden. As our Sun's magnetic field evolves into the active part of its 11-year cycle, auroras near both of Earth's poles are sure to become more frequent.
| << Previous APOD | This Day in APOD | Next APOD >> |