Page 1 of 2
Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 4:36 am
by bystander
Have you seen a great image or video somewhere that you think would make a great APOD? Nominate it for APOD! Please post as much information here as you have about the image/video with a link to any source(s) for it you know of here, and the editors will take a look.
When posting the image itself, please do not post anything larger than a thumbnail here; please honor the copyright holder's copyright.
Please keep hotlinked images under 500K.
Thank you!
<< Previously
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 10:02 pm
by starsurfer
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 10:06 pm
by starsurfer
Dr 29 and IPHASX J193308.9+15535
https://www.imagingdeepspace.com/dr-29.html
Data: Peter Goodhew
Processing: Marcel Drechsler
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 10:12 pm
by starsurfer
NGC 1316-7
https://www.hansonastronomy.com/ngc-1316-new
Data: Martin Pugh
Processing: Mark Hanson
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 10:15 pm
by starsurfer
Whirlpool Galaxy (M51)
http://www.starpointing.com/ccd/m51.html
Copyright: Fabian Neyer
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 01, 2022 10:20 pm
by starsurfer
Eta Carinae Nebula (NGC 3372)
http://www.cielaustral.com/galerie/photo136.htm
Copyright: Ciel Austral
ESO: The Golden Era to Study Stellar Births (M61)
Posted: Tue Aug 02, 2022 5:01 am
by bystander
The Golden Era to Study Stellar Births
ESO Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 01
This week, we feature an image of the spiral galaxy
NGC 4303, also known as
Messier 61, which is one of the largest galactic members of the
Virgo Cluster. Being a so-called
starburst galaxy, it has an unusually high amount of stars being born, and has been
used by astronomers as a laboratory to better understand the fascinating phenomena of star formation.
Stars form when clouds of cold gas collapse. The energetic radiation from newly born stars will heat and
ionise the surrounding remaining gas. The ionised gas will shine, acting as a beacon of ongoing star formation. In this stunning and jewel-like image, this glowing gas can be seen as the whirlpool of gold: the direct traces of stars being born.
The golden glow is a result of combining observations taken at different wavelengths of light with the Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (
MUSE) instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope (
VLT) in Chile. Here gas clouds of ionised oxygen, hydrogen and sulphur are shown in blue, green and red, respectively. The observations are done as part of the Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS (
PHANGS) project, aiming to reveal nearby galaxies across all wavelengths of the
electromagnetic spectrum. ...
ESA: Star-Studded Skyfield (NGC 6638)
Posted: Tue Aug 02, 2022 5:15 am
by bystander
Star-Studded Skyfield
ESA Hubble Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 01
Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen
This star-studded image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows the heart of the
globular cluster NGC 6638 in the constellation
Sagittarius. The star-strewn observation highlights the density of stars at the heart of
globular clusters, which are stable, tightly bound clusters of tens of thousands to millions of
stars. To capture the data in this image, Hubble used two of its cutting-edge astronomical instruments: Wide Field Camera 3 (
WFC3) and the Advanced Camera for Surveys (
ACS).
Hubble revolutionised the study of globular clusters, as it is almost impossible to clearly distinguish the stars in globular clusters with ground-based telescopes. The blurring caused by Earth’s atmosphere makes it impossible to tell one star from another, but from Hubble’s location in low Earth orbit the atmosphere no longer poses a problem. As a result, Hubble has been used to study what kind of stars globular clusters are made up of, how they evolve, and the role of gravity in these dense systems.
The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope will further our understanding of globular clusters by peering into those globular clusters that are currently obscured by dust. Webb will predominantly observe at
infrared wavelengths, which are less affected by the gas and dust surrounding newborn stars. This will allow astronomers to inspect star clusters that are freshly formed, providing insights into stellar populations before they have a chance to evolve.
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sat Aug 06, 2022 10:10 pm
by starsurfer
NGC 225 and vdB4
http://www.capella-observatory.com/Imag ... a/vdB4.htm
Copyright: Josef Pöpsel, Stefan Binnewies and Frank Sackenheim
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sat Aug 06, 2022 10:16 pm
by starsurfer
Gum 54 region
http://www.atacama-photographic-observa ... php?id=114
Copyright: Thierry Demange, Richard Galli and Thomas Petit
ESO: The Hunt for Exoplanets (NGTS)
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 1:51 pm
by bystander
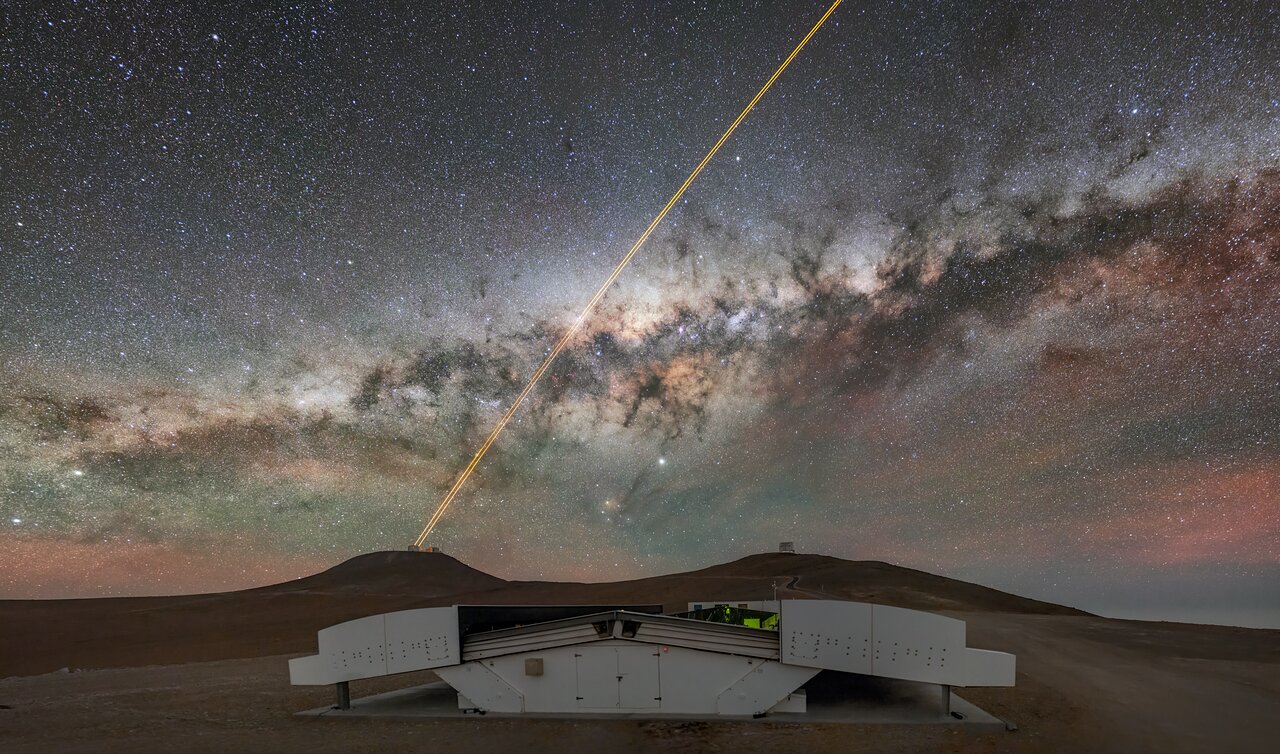
The Hunt for Exoplanets
ESO Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 08
This Picture of the Week shows a stunning view of the Milky Way as it stretches over the Atacama Desert, home to ESO’s
Paranal Observatory. In the foreground, we also get a glimpse of the planet hunter
NGTS, the Next Generation Transit Survey.
NGTS, built by a collaboration of UK, Swiss and German institutions, consists of 12 telescopes that continuously monitor the sky, looking for dips in the brightness of hundreds of thousands of stars. As an exoplanet
transits between its host star and us, it dims the light reaching us, which can be picked up by NGTS. The survey specialises in looking for
super-Earths, exoplanets more massive than our home planet but lighter than an ice giant like Neptune. NGTS also works in tandem with ESO telescopes, like the ones visible in the background: the Very Large Telescope (
VLT, with its
adaptive optics lasers) and the Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (
VISTA) to the right.
When NGTS detects new planet candidates, ESO instruments, such as the exoplanet specialists
HARPS at ESO’s
La Silla Observatory or
ESPRESSO at the VLT, can do follow-up observations. From these observations we can learn about the masses of these exoplanets and compositions of their atmospheres. With the combined power of these facilities, the exoplanets of the Milky Way are being studied with the highest possible precision and detail there is.
ESA: Celestial Cloudscape in the Orion Nebula
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 2:14 pm
by bystander
Celestial Cloudscape in the Orion Nebula
ESA Hubble Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 08
This celestial cloudscape from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope captures the colourful region surrounding the
Herbig-Haro object HH 505. Herbig-Haro objects are luminous regions surrounding newborn stars, and are formed when stellar winds or jets of gas spewing from these newborn stars form shockwaves colliding with nearby gas and dust at high speeds. In the case of HH 505, these outflows originate from the star IX Ori, which lies on the outskirts of the
Orion Nebula around 1000 light-years from Earth. The outflows themselves are visible as gracefully curving structures at the top and bottom of this image, and are distorted into sinuous curves by their interaction with the large-scale flow of gas and dust from the core of the Orion Nebula.
This observation was captured with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (
ACS) by astronomers studying the properties of outflows and protoplanetary discs. The Orion Nebula is awash in intense ultraviolet radiation from bright young stars. The shockwaves formed by the outflows are brightly visible to Hubble, but the slower-moving currents of stellar material are also highlighted by this radiation. That allows astronomers to directly observe jets and outflows and learn more about their structures.
The Orion Nebula is a dynamic region of dust and gas where thousands of stars are forming, and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. As a result, it is one of the most scrutinised areas of the night sky and has often been a
target for Hubble. This observation was also part of a spellbinding Hubble
mosaic of the Orion Nebula, which combined 520 ACS images in five different colours to create the sharpest view ever taken of the region.
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 10:12 pm
by starsurfer
Orion Nebula (M42) region
https://www.astrobin.com/394510/
Copyright: Stefan Westphal
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 10:14 pm
by starsurfer
Hyades region
https://www.astrobin.com/401845/
Copyright: Tommy Nawratil
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 10:16 pm
by starsurfer
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 10:18 pm
by starsurfer
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 08, 2022 10:20 pm
by starsurfer
NOIRLab: Colliding Galaxies Dazzle (Butterfly Galaxies)
Posted: Tue Aug 09, 2022 8:53 pm
by bystander
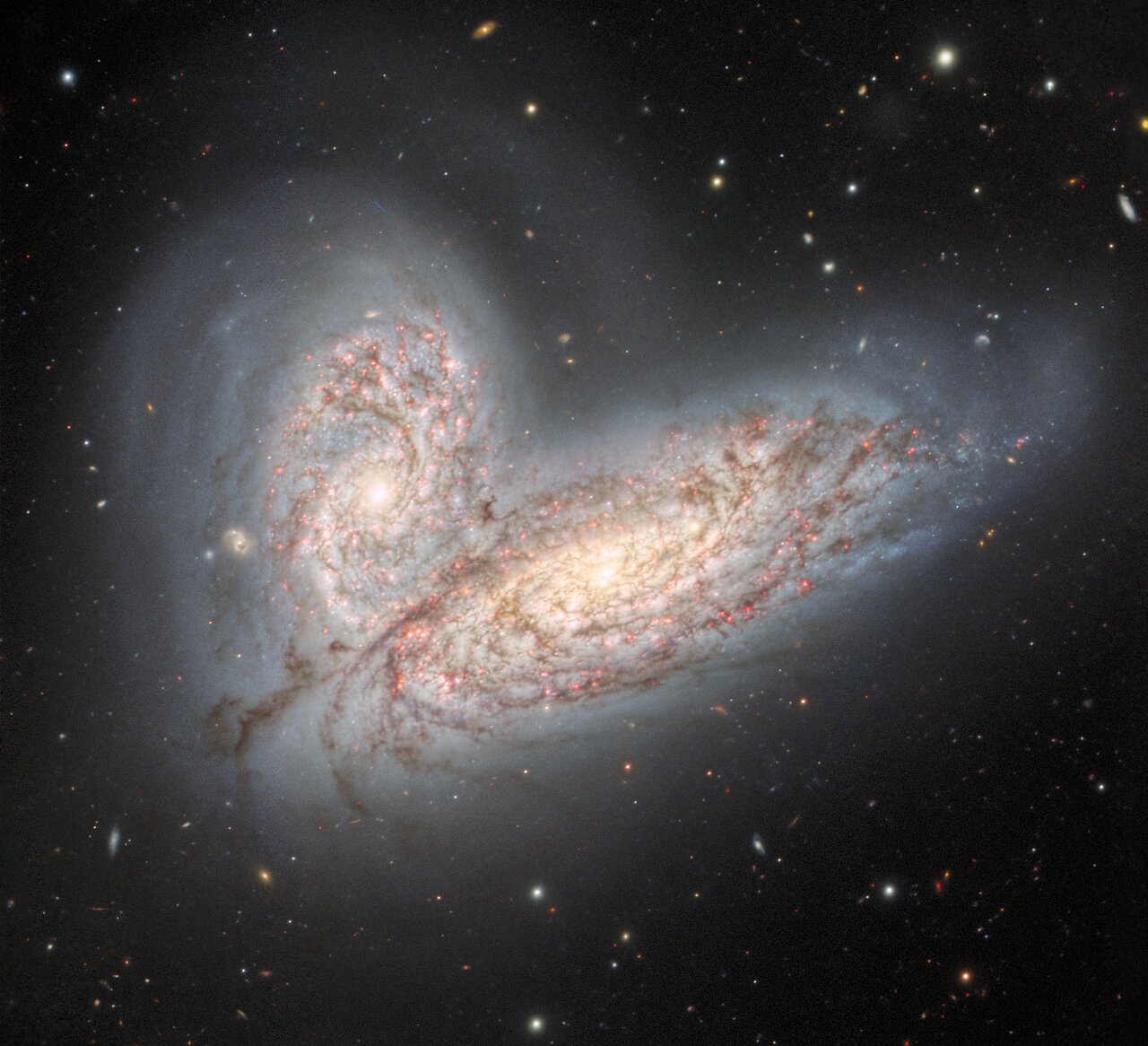
Colliding Galaxies Dazzle
Gemini North | NOIRLab | 2022 Aug 09
An evocative new image captured by the Gemini North telescope in Hawai‘i reveals a pair of interacting spiral galaxies — NGC 4568 and NGC 4567 — as they begin to clash and merge. These galaxies are entangled by their mutual gravitational field and will eventually combine to form a single elliptical galaxy in around 500 million years. Also visible in the image is the glowing remains of a supernova that was detected in 2020.
Gemini North, one of the twin telescopes of the International
Gemini Observatory, operated by NSF’s
NOIRLab, has observed the initial stages of a cosmic collision approximately 60 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation
Virgo. The two stately spiral galaxies,
NGC 4568 (bottom) and
NGC 4567 (top), are poised to undergo one of the most spectacular events in the Universe, a galactic merger. At present, the centers of these galaxies are still 20,000 light-years apart (about the distance from Earth to the center of the Milky Way) and each galaxy still retains its original, pinwheel shape. Those placid conditions, however, will change.
As
NGC 4568 and NGC 4567 draw together and coalesce, their dueling gravitational forces will trigger bursts of intense stellar formation and wildly distort their once-majestic structures. Over millions of years, the galaxies will repeatedly swing past each other in ever-tightening loops, drawing out long streamers of stars and gas until their individual structures are so thoroughly mixed that a single, essentially spherical, galaxy emerges from the chaos. By that point, much of the gas and dust (the fuel for star formation) in this system will have been used up or blown away. ...
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sat Aug 13, 2022 7:50 am
by AVAO
The way into the future of our sun
https://www.universetoday.com/157122/th ... -will-die/
The path of similar stars shows the Sun’s fate.
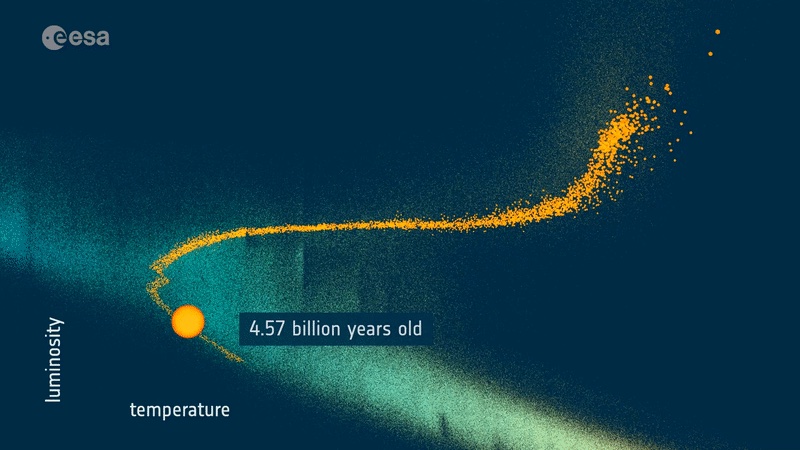
Credit: ESA/Gaia/DPAC, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The Gaia team also found nearly 6,000 stars that are near twins of the Sun, having similar mass, temperature, composition, and age. By observing these stars, astronomers will get a better understanding of whether our Sun is typical. For example, do these other stars have solar cycles similar to the Sun? Do some have periods of intense solar flares or are they fairly stable like the Sun?
With so much gathered data, Gaia is revealing new details about our own star, how it may behave in the near future, and how it will die in the far future. We’ve long known the end is nigh for the Sun, but we’re beginning to learn just how and when the end will come.
Reference: Creevey, O. L., et al. “Gaia Data Release 3: Astrophysical parameters inference system (Apsis) I–methods and content overview.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.05864 (2022).
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sun Aug 14, 2022 10:25 pm
by starsurfer
NGC 972
https://esahubble.org/images/potw1926a/
Copyright: ESA/Hubble, NASA, L. Ho
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sun Aug 14, 2022 10:27 pm
by starsurfer
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Sun Aug 14, 2022 10:54 pm
by barretosmed
X AND V LUNAR
BEST DETAILS
https://www.astrobin.com/full/jqcuwu/B/
EQUIPMENT:
Esprit 150mm
asi 6200mc
Mount cem120
LOCATION: Munhoz - MG - BRAZIL
DATES: 08/04/2022
Author: Fernando Oliveira de Menezes
(Organizing author of the book Amateur Astrophotography in Brazil)
https://clubedeautores.com.br/livro/ast ... -no-brasil
ESO: A Distant Beacon (VLT)
Posted: Mon Aug 15, 2022 2:42 pm
by bystander
A Distant Beacon
ESO Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 15
Cerro Armazones, in Chile's Atacama Desert, is the site of ESO’s upcoming giant, the Extremely Large Telescope (
ELT). In this image, we see the road leading up to this 3000m-high mountain, and in the distance, ESO’s Very Large Telescope (
VLT). The
lasers of the VLT reach towards the sky, parallel to the Milky Way. Cerro Armazones was actually the first suggested site for the VLT, and now the mountain will finally get a telescope of its own.
Working at high altitude is not easy, but Cerro Armazones is both dry and has almost no artificial
light pollution, making it a perfect site with excellent conditions for the world’s biggest eye on the sky. In this picture we see a red shimmer illuminating the dark sky, a natural phenomenon called
airglow.
With an anticipated first light later this decade, and equipped with a range of
scientific instruments, the ELT will be able to probe the Milky Way and its
stars and
planets, as well as
look back in time to unravel the mysteries of cosmos. One can truly say that good things come to those who wait.
ESA: Hubble Spies a Scintillating Globular Cluster (NGC 6540)
Posted: Mon Aug 15, 2022 2:55 pm
by bystander
Hubble Spies a Scintillating Globular Cluster
ESA Hubble Picture of the Week | 2022 Aug 15
Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen
This scintillating image showcases the
globular cluster NGC 6540 in the constellation
Sagittarius, which was captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s
Wide Field Camera 3 and
Advanced Camera for Surveys. These two instruments have slightly different fields of view — which determines how large an area of sky each instrument captures. This composite image shows the star-studded area of sky that was captured in both instruments’ field of view.
NGC 6540 is a globular cluster, a stable, tightly bound multitude of
stars. The populations of these clusters can range from tens of thousands to millions of stars, all of which are trapped in a closely-packed group by their mutual gravitational attraction.
The brightest stars in this image are adorned with prominent cross-shaped patterns of light known as
diffraction spikes. These astronomical embellishments are a type of imaging artefact, meaning that they are caused by the structure of Hubble rather than the stars themselves. The path taken by the starlight as it enters the telescope is slightly disturbed by its internal structure, causing bright objects to be surrounded by spikes of light.
Hubble peered into the heart of NGC 6540 to help astronomers measure the ages, shapes, and structures of globular clusters towards the centre of the Milky Way. The gas and dust shrouding the centre of our
galaxy block some of the light from these clusters, as well as subtly changing the colours of their stars. Globular clusters contain insights into the earliest history of the Milky Way, and so studying them can help astronomers understand how our galaxy has evolved.
Re: Found Images: 2022 August
Posted: Mon Aug 15, 2022 10:10 pm
by starsurfer
Abell 43
https://www.astrobin.com/r7icd0/
Copyright: Boris Chausov





