APOD Retrospective: February 14
Posted: Tue Feb 14, 2012 4:36 am
| << Previous | Index | Next >> |
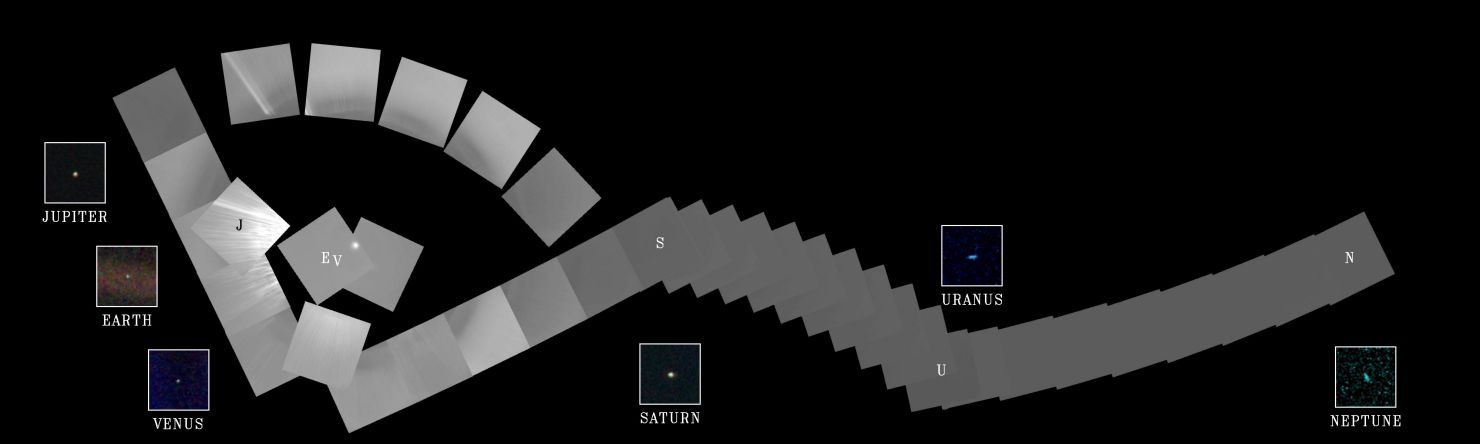
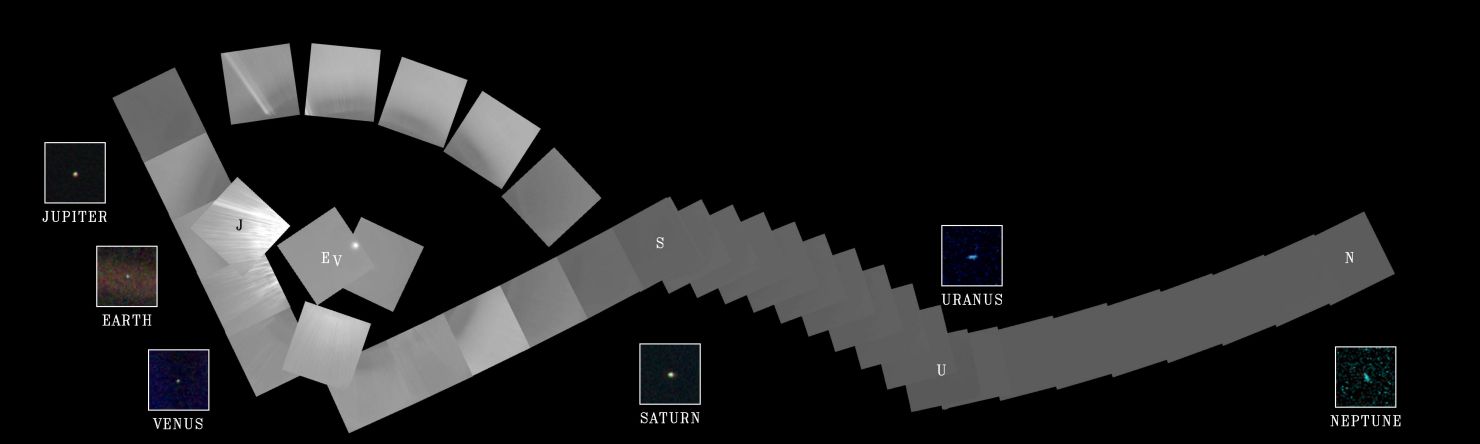
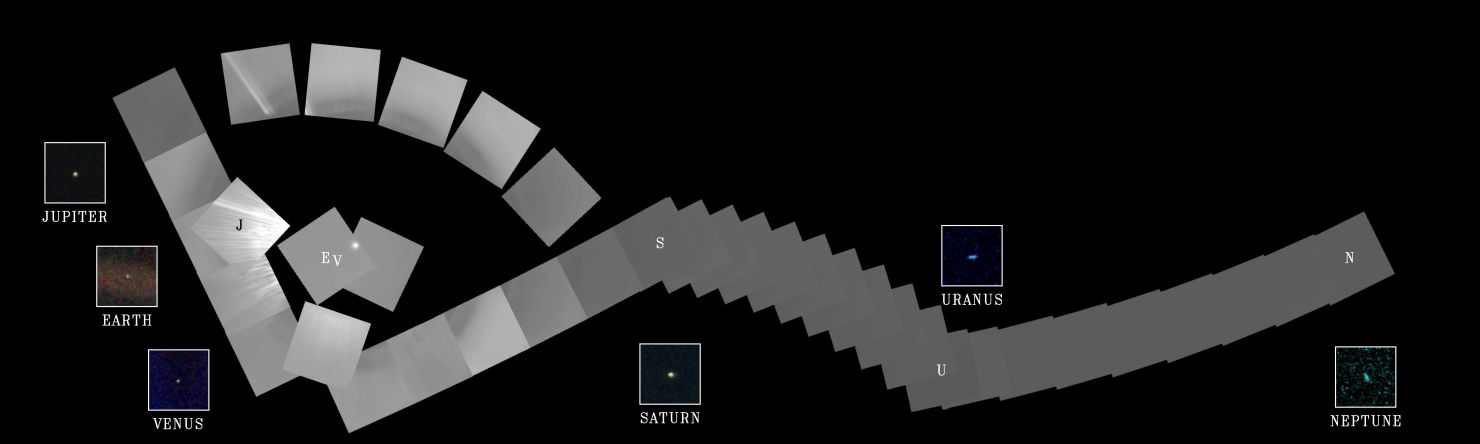
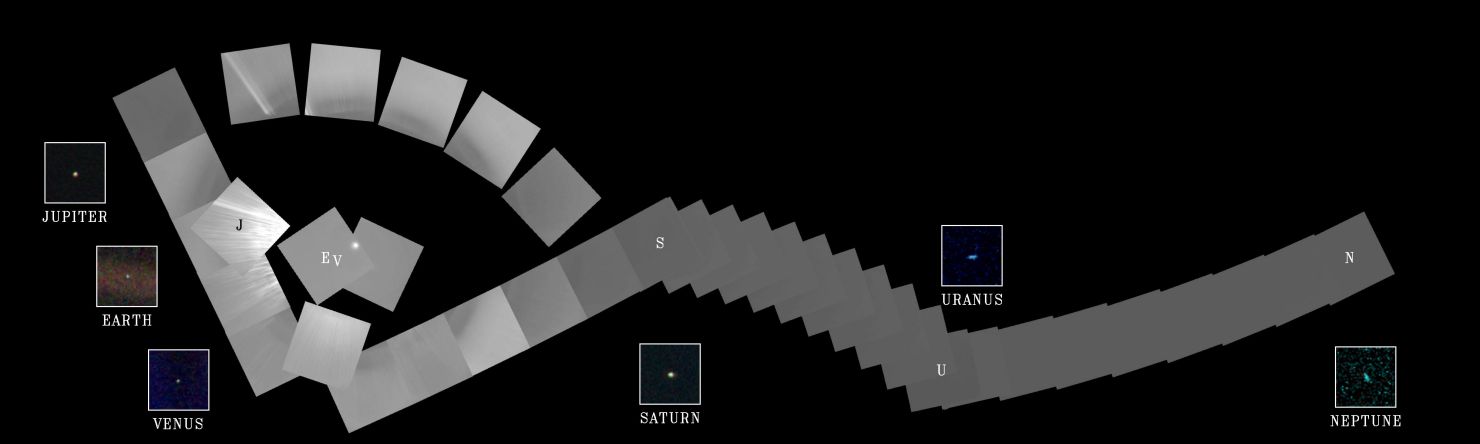
2015 On another Valentine's Day 25 years ago, cruising four billion miles from the Sun, the Voyager 1 spacecraft looked back one last time to make this first ever Solar System family portrait. The complete portrait is a 60 frame mosaic made from a vantage point 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. In it, Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the inner Solar System at the left, linking up with gas giant Neptune, the Solar System's outermost planet, at the far right. Positions for Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are indicated by letters, while the Sun is the bright spot near the center of the circle of frames. The inset frames for each of the planets are from Voyager's narrow field camera. Unseen in the portrait are Mercury, too close to the Sun to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight scattered in the camera's optical system. Closer to the Sun than Neptune at the time, small, faint Pluto's position was not covered.
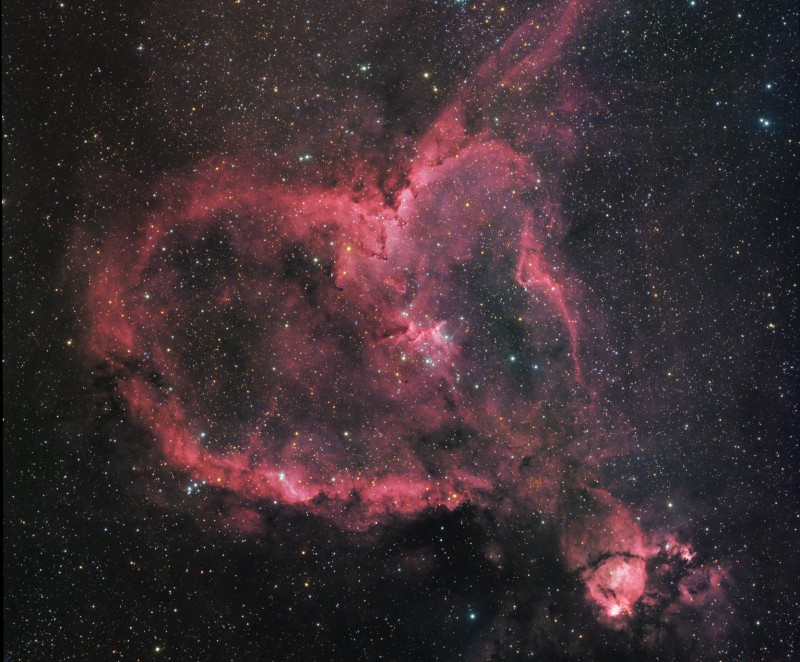
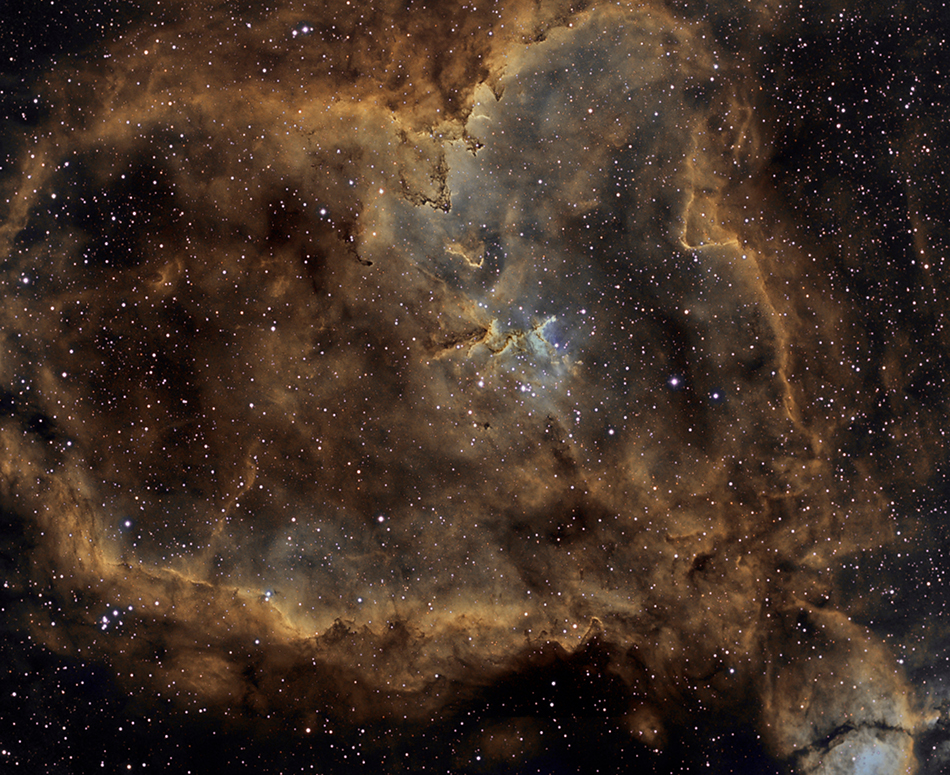
2014 Sprawling across almost 200 light-years, emission nebula IC 1805 is a mix of glowing interstellar gas and dark dust clouds about 7,500 light-years away in the Perseus spiral arm of our galaxy. Stars were born in this region whose nickname, the Heart Nebula, derives from its Valentine's-Day-appropriate shape. The clouds themselves are shaped by stellar winds and radiation from massive hot stars in the nebula's newborn star cluster Melotte 15 about 1.5 million years young. This deep telescopic image maps the pervasive light of narrow emission lines from atoms in the nebula to a color palette made popular in Hubble images of star forming regions. The field of view spans about two degrees on the sky or four times the diameter of a full moon. The cosmic heart is found in the constellation of Cassiopeia, the boastful mythical Queen of Aethiopia.
2013 On another Valentine's Day (February 14, 1990), cruising four billion miles from the Sun, the Voyager 1 spacecraft looked back to make this first ever family portrait of our Solar System. The complete portrait is a 60 frame mosaic made from a vantage point 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. In it, Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the inner Solar System at the left, linking up with gas giant Neptune, at the time the Solar System's outermost planet, at the far right. Positions for Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are indicated by letters, while the Sun is the bright spot near the center of the circle of frames. The inset frames for each of the planets are from Voyager's narrow field camera. Unseen in the portrait are Mercury, too close to the Sun to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight scattered in the camera's optical system. Small, faint Pluto's position was not covered.
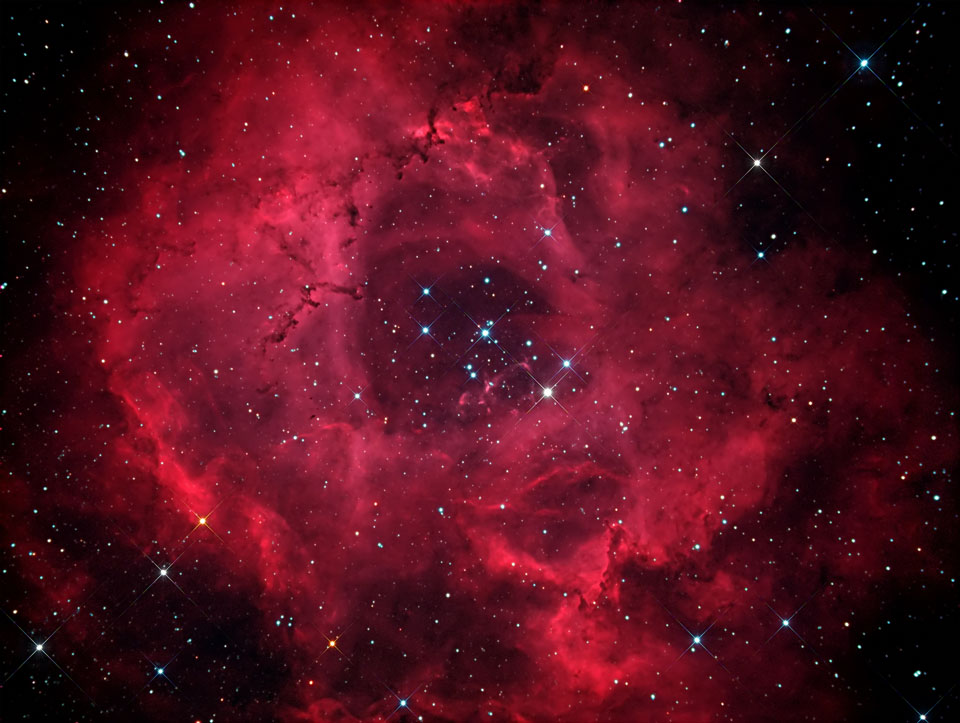
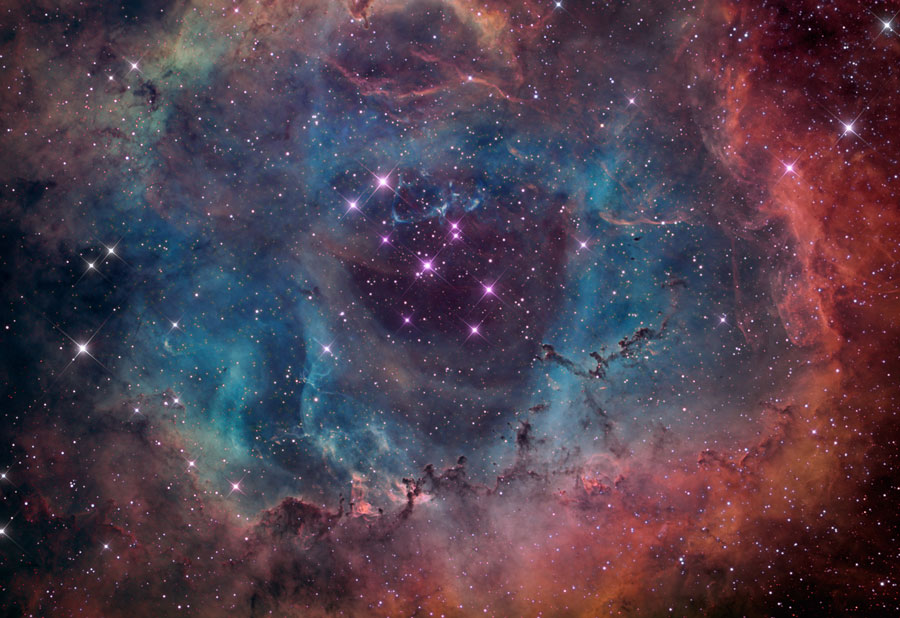
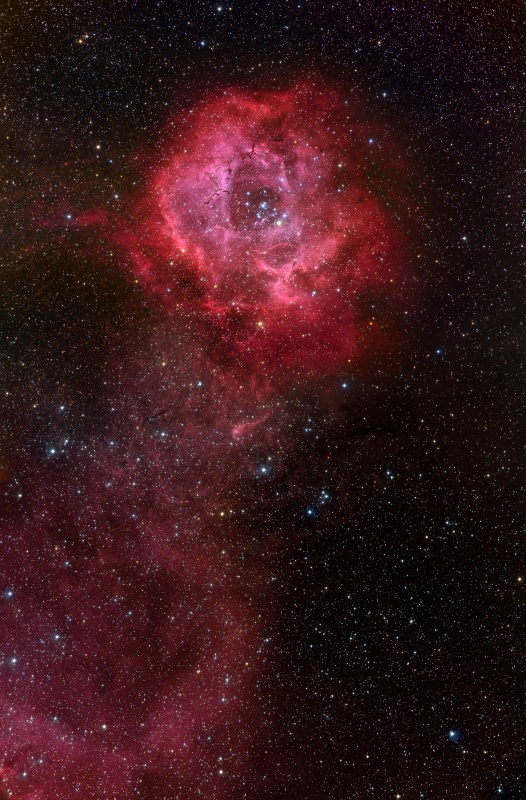
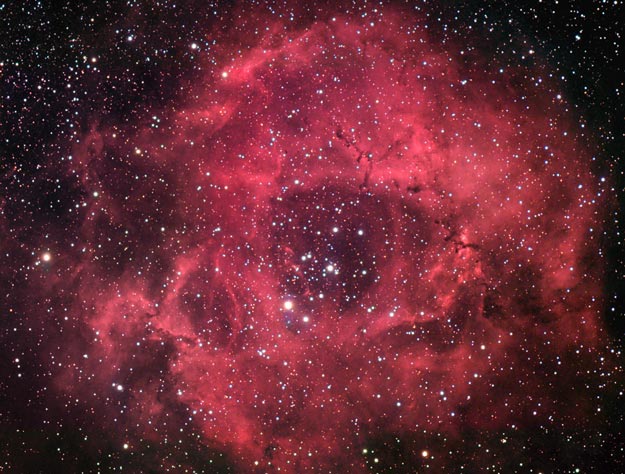
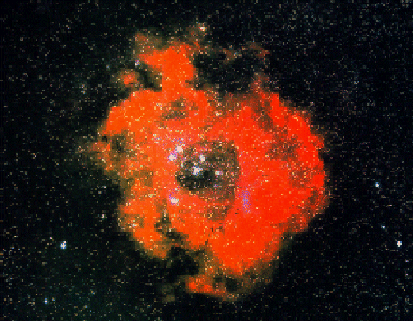
2012 The Rosette Nebula is not the only cosmic cloud of gas and dust to evoke the imagery of flowers -- but it is the most famous. At the edge of a large molecular cloud in Monoceros, some 5,000 light years away, the petals of this rose are actually a stellar nursery whose lovely, symmetric shape is sculpted by the winds and radiation from its central cluster of hot young stars. The stars in the energetic cluster, cataloged as NGC 2244, are only a few million years old, while the central cavity in the Rosette Nebula, cataloged as NGC 2237, is about 50 light-years in diameter. The nebula can be seen firsthand with a small telescope toward the constellation of the Unicorn (Monoceros).
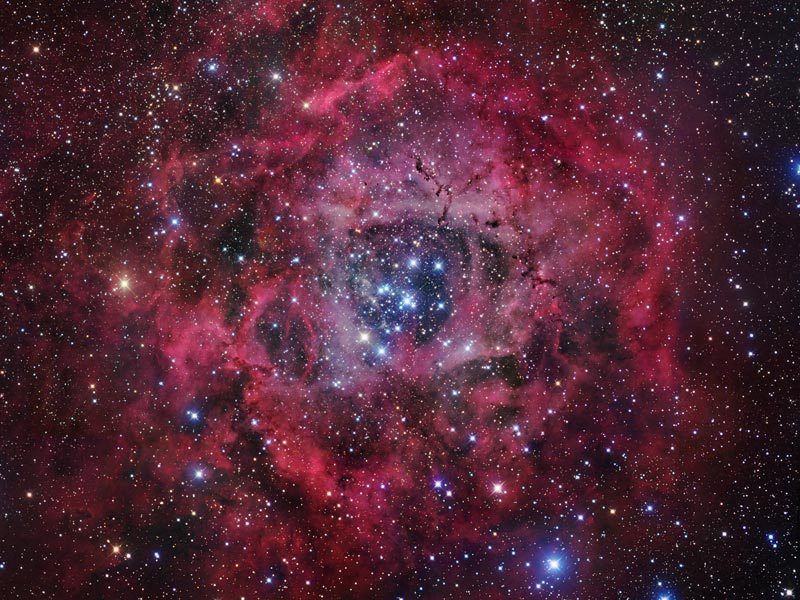
2011 Would the Rosette Nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars formed about four million years ago from the nebular material and their stellar winds are clearing a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow. The Rosette Nebula spans about 100 light-years across, lies about 5000 light-years away, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of the Unicorn (Monoceros).
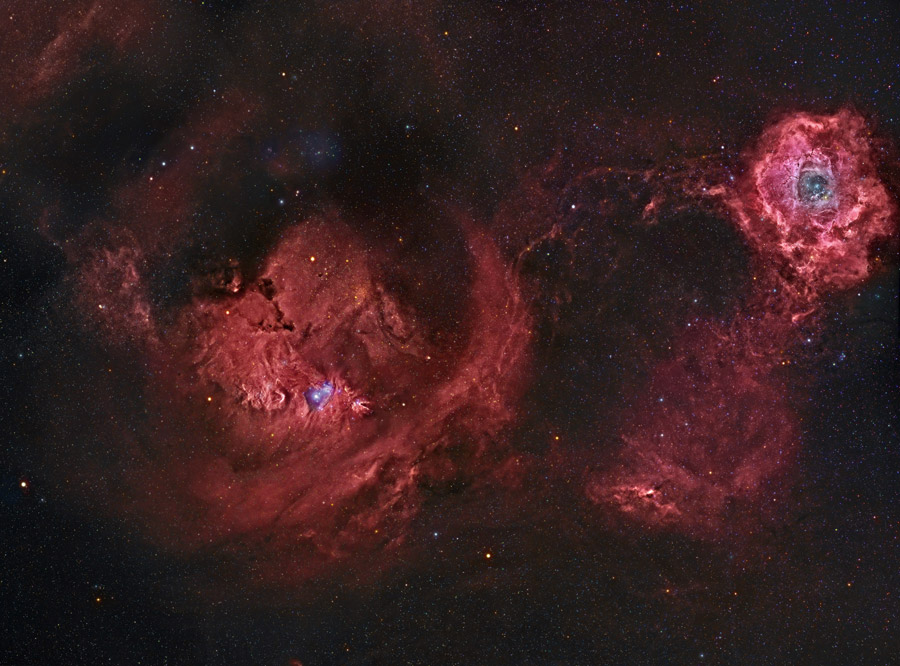
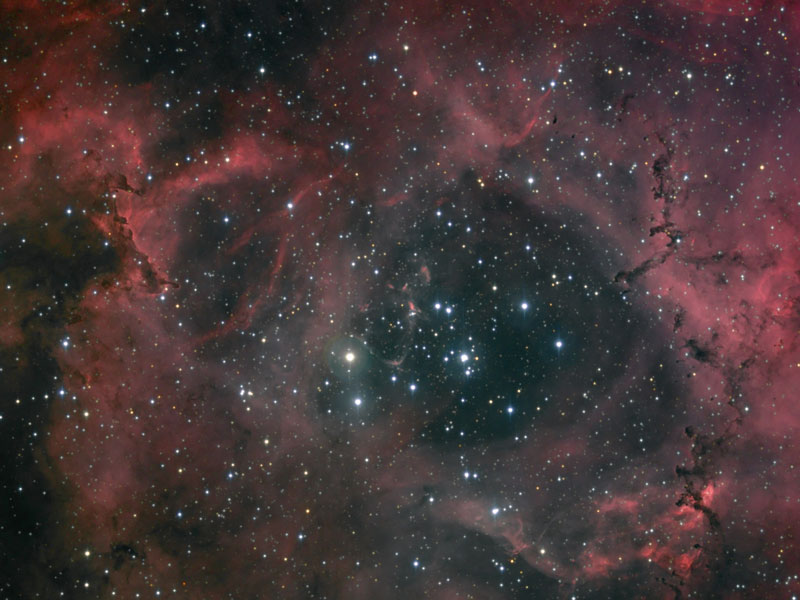
2010 What surrounds the florid Rosette nebula? To better picture this area of the sky, the famous flowery emission nebula on the far right has been captured recently in a deep and dramatic wide field image that features several other sky highlights. Designated NGC 2237, the center of the Rosette nebula is populated by the bright blue stars of open cluster NGC 2244, whose winds and energetic light are evacuating the nebula's center. Below the famous flower, a symbol of Valentine's Day, is a column of dust and gas that appears like a rose's stem but extends hundreds of light years. Across the above image, the bright blue star just left and below the center is called S Monocerotis. The star is part of the open cluster of stars labelled NGC 2264 and known as the Snowflake cluster. To the right of S Mon is a dark pointy featured called the Cone nebula, a nebula likely shaped by winds flowing out a massive star obscured by dust. To the left of S Mon is the Fox Fur nebula, a tumultuous region created by the rapidly evolving Snowflake cluster. The Rosette region, at about 5,000 light years distant, is about twice as far away as the region surrounding S Mon. The entire field can be seen with a small telescope toward the constellation of the Unicorn (Monoceros).
2009 Sprawling across almost 200 light-years, emission nebula IC 1805 is a mix of glowing interstellar gas and dark dust clouds. Derived from its Valentine's-Day-approved shape, its nickname is the Heart Nebula. About 7,500 light-years away in the Perseus spiral arm of our galaxy, stars were born in IC 1805. In fact, near the cosmic heart's center are the massive hot stars of a newborn star cluster also known as Melotte 15, about 1.5 million years young. A little ironically, the Heart Nebula is located in the constellation Cassiopeia. From Greek mythology, the northern constellation is named for a vain and boastful queen. This deep view of the region around the Heart Nebula, cropped from a larger mosaic, spans about 2.5 degrees on the sky or about 5 times the diameter of the Full Moon.
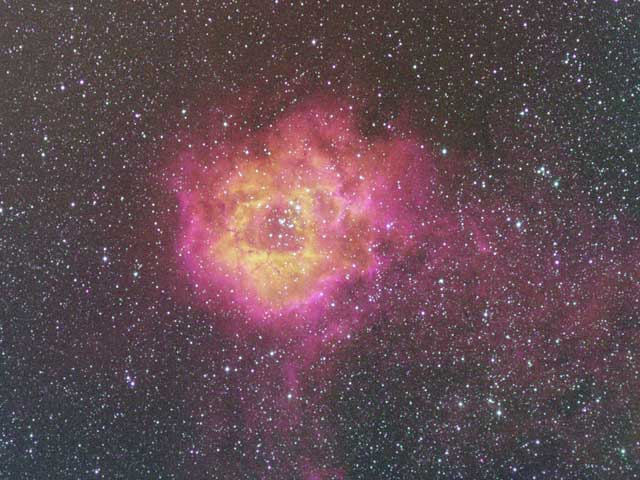
2008 The Rosette Nebula (aka NGC 2237) is not the only cosmic cloud of gas and dust to evoke the imagery of flowers. But it is the one most often suggested as a suitable astronomy image for Valentine's Day. Of the many excellent Rosette Nebula pictures submitted to APOD editors, this view seemed most appropriate, with a long stem of glowing hydrogen gas in the region included in the composition. At the edge of a large molecular cloud in Monoceros, some 5,000 light years away, the petals of this rose are actually a stellar nursery whose lovely, symmetric shape is sculpted by the winds and radiation from its central cluster of hot young stars. The stars in the energetic cluster, cataloged as NGC 2244, are only a few million years old, while the central cavity in the Rosette Nebula is about 50 light-years in diameter. Happy Valentine's Day!
2007 Would the Rosette Nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of the this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars formed about four million years ago from the nebular material and their stellar winds are clearing a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow. The Rosette Nebula spans about 100 light-years across, lies about 5000 light-years away, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of Monoceros.
2006 What creates the cosmic dust sculptures in the Rosette Nebula? Noted for the common beauty of its overall shape, parts of the Rosette Nebula, also known as NGC 2244, show beauty even when viewed up close. Visible above are globules of dark dust and gas that are slowly being eroded away by the energetic light and winds by nearby massive stars. Left alone long enough, the molecular-cloud globules would likely form stars and planets. The Rosette Nebula spans about 50 light-years across, lies about 4,500 light-years away, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of Monoceros. Happy Valentine's Day from the folks at APOD.
2005 Would the Rosette Nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of the this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars formed about four million years ago from the nebular material and their stellar winds are clearing a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow. The Rosette Nebula spans about 100 light-years across, lies about 5000 light-years away, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of Monoceros.
2004 On another Valentine's Day (February 14, 1990), cruising four billion miles from the Sun, the Voyager 1 spacecraft looked back to make this first ever family portrait of our Solar System. The complete portrait is a 60 frame mosaic made from a vantage point 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the inner Solar System (far left) linking up with gas giant Neptune, at the time the Solar System's outermost planet (scroll right). Positions for Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are indicated by the corresponding letters while the Sun is the bright spot near the center of the circle of frames. The inset frames for each of the planets are from Voyager's narrow field camera. Unseen in the portrait are Mercury, too close to the Sun to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight scattered in the camera's optical system. Small, faint Pluto's position was not covered.
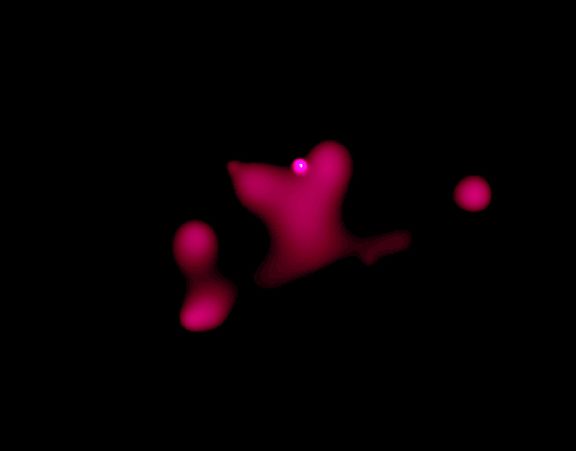
2003 Yes, it's Valentine's Day (!) and looking toward star cluster NGC 346 in our neighboring galaxy the Small Magellanic Cloud, astronomers have noted this heart-shaped cloud of hot, x-ray emitting gas in the cluster's central region. The false-color Chandra Observatory x-ray image also shows a strong x-ray source just above the heart-shaped cloud which corresponds to HD 5980, a remarkable, massive binary star system that lies within the cluster. HD 5980 has been known to undergo dramatic brightness variations, in 1994 briefly outshining all other stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud, and has been likened to the luminous, eruptive variable star Eta Carinae in our own Milky Way galaxy. At about 100 light-years across, NGC 346's heart-shaped cloud is probably the result of an ancient supernova explosion. Alternatively it may have been produced during past eruptions from the HD 5980 system, analogous to the nebula associated with Eta Carinae.
2002 On another Valentine's Day (February 14, 1990), cruising four billion miles from the Sun, the Voyager 1 spacecraft looked back to make this first ever family portrait of our Solar System. The complete portrait is a 60 frame mosaic made from a vantage point 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the inner Solar System (far left) linking up with gas giant Neptune, at the time the Solar System's outermost planet (scroll right). Positions for Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are indicated by the corresponding letters while the Sun is the bright spot near the center of the circle of frames. The inset frames for each of the planets are from Voyager's narrow field camera. Unseen in the portrait are Mercury, too close to the Sun to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight scattered in the camera's optical system. Small, faint Pluto's position was not covered.
2001 Would the Rosette Nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of the this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars formed about four million years ago from the nebular material and their stellar winds are clearing a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow. The Rosette Nebula spans about 100 light-years across, lies about 5000 light-years away, and can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of Monoceros.
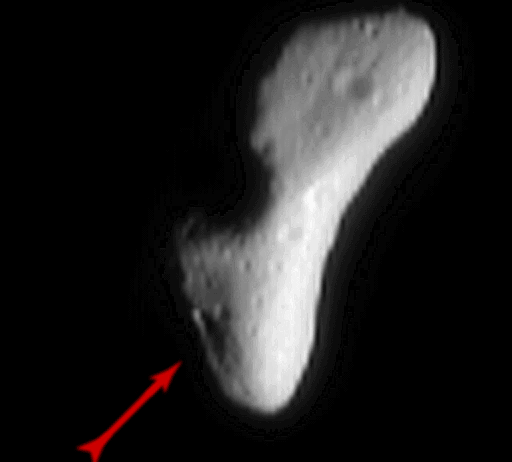
2000 Maybe the Moon owns our hearts, but this won't stop the occasional asteroid from sending us a valentine. Friday, to the surprise of many, the NEAR mission on approach to asteroid 433 EROS photographed what appears to be a heart-shaped depression. After NEAR reaches the asteroid today, NASA plans a series of maneuvers to make the robot spacecraft the first ever to orbit an asteroid. More detailed pictures will soon be taken of the 33 kilometer long asteroid EROS and this 5 kilometer long depression. Most likely, fortuitous lighting and viewing angles accentuate the apparent heart shape -- but don't tell the Moon.
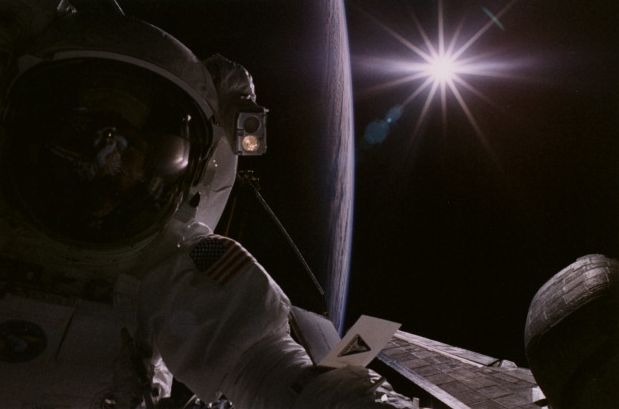
1999 In low Earth orbit there is not enough atmosphere to diffuse and scatter sunlight, so shadows are black and the sky is dark - even when the Sun shines. The harsh lighting produced this dramatic effect as mission specialist Gregory Harbaugh photographed colleague Joseph Tanner during their second spacewalk to service the Hubble Space Telescope in February 1997. The aft section of the Space Shuttle Discovery is visible in the background with the Sun hanging over a delicate crescent of the Earth's limb. A checklist is attached to Tanner's left arm, and Harbaugh's reflection is just visible in Tanner's visor.
1998 Would the Rosette Nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of the this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars recently formed from the nebular material and their stellar "wind" has cleared a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow.
1997 Globular clusters once ruled the Milky Way. Back in the old days, back when our Galaxy first formed, perhaps thousands of globular clusters roamed our Galaxy. Today, there are perhaps 200 left. Many globular clusters were destroyed over the eons by repeated fateful encounters with each other or the Galactic center. Surviving relics are older than any earth fossil, older than any other structures in our Galaxy, and limit the universe itself in raw age. There are few, if any, young globular clusters in our Milky Way Galaxy because conditions are not ripe for more to form. But things are different next door - in the neighboring LMC galaxy. Pictured above is a "young" globular cluster residing there: NGC 1818. Recent observations show it formed only about 40 million years ago - just yesterday compared to the 12 billion year ages of globular clusters in our own Milky Way
1996 Would the Rosette nebula by any other name look as sweet? The bland New General Catalog designation of NGC 2237 doesn't appear to diminish the appearance of the this flowery emission nebula. Inside the nebula lies an open cluster of bright young stars designated NGC 2244. These stars recently formed from the nebular material and their stellar "wind" has cleared a hole in the nebula's center, insulated by a layer of dust and hot gas. Ultraviolet light from the hot cluster stars causes the surrounding nebula to glow.
| << Previous | Index | Next >> |