http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nut_(goddess) wrote:
[img3="
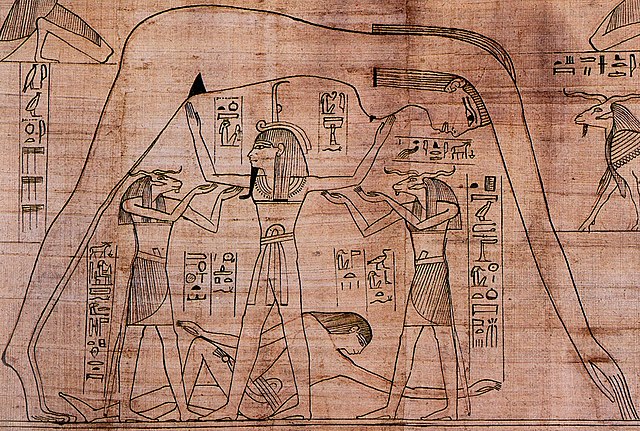
The Sky Goddess Nut arched protectively over the Earth and all of its inhabitants. Nut was seen as a friend and protector of the dead, who appealed to her as a child appeals to its mother: "O my Mother Nut, stretch Yourself over me, that I may be placed among the imperishable stars which are in You, and that I may not die." Nut was thought to draw the dead into her star-filled sky, and refresh them with food and wine: "I am Nut, and I have come so that I may enfold and protect you from all things evil." She was often painted on the inside lid of the sarcophagus, protecting the deceased. The vault of tombs often were painted dark blue with many stars as a representation of Nut."]
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/c ... ss_nut.jpg[/img3]
<<Nut or Neuth (also spelled Nuit or Newet) was the goddess of the sky in the Ennead of Egyptian mythology. She was seen as a star-covered nude woman arching over the earth, or as a cow. Nut and her brother/husband, Geb, may be considered enigmas in the world of mythology. In direct contrast to most other mythologies which usually develop a sky father associated with an Earth mother (or Mother Nature), she personified the sky and he the Earth.
Nut is a daughter of Shu and Tefnut. Her name is translated to mean 'sky' and she is considered one of the oldest deities among the Egyptian pantheon, with her origin being found on the creation story of Heliopolis. She was originally the goddess of the nighttime sky, but eventually became referred to as simply the sky goddess. Her headdress was the hieroglyphic of part of her name, a pot, which may also symbolize the uterus. Mostly depicted in nude human form, Nut was also sometimes depicted in the form of a cow whose great body formed the sky and heavens, a sycamore tree, or as a giant sow, suckling many piglets (representing the stars).
A sacred symbol of Nut was the ladder, used by Osiris to enter her heavenly skies. This ladder-symbol was called maqet and was placed in tombs to protect the deceased, and to invoke the aid of the deity of the dead.
Ra, the sun god, was the second to rule the world, according to the reign of the gods. Ra was a strong ruler but he feared anyone taking his throne. When he discovered that Nut was to have children he was furious. He decreed, "Nut shall not give birth any day of the year." At that time, the year was only 360 days. Nut spoke to Thoth, god of wisdom, and he had a plan. Thoth gambled with Khonshu, god of the moon, whose light rivaled that of Ra's. Every time Khonshu lost, he had to give Thoth some of his moonlight. Khonshu lost so many times that Thoth had enough moonlight to make 5 extra days. Since these days were not part of the year, Nut could have her children. She had 5: Osiris, Horus the Elder, Set, Isis, and Nepthys. When Ra found out, he was furious. He separated Nut from her husband Geb for all eternity. Her father, Shu, was to keep them apart. Still, Nut did not regret her decision.
Nut was the goddess of the sky and all heavenly bodies, a symbol of protecting the dead when they enter the after life. According to the Egyptians, during the day, the heavenly bodies—such as the sun and moon—would make their way across her body. Then, at dusk, they would be swallowed, pass through her belly during the night, and be reborn at dawn.
Nut is also the barrier separating the forces of chaos from the ordered cosmos in the world. She was pictured as a woman arched on her toes and fingertips over the earth; her body portrayed as a star-filled sky. Nut’s fingers and toes were believed to touch the four cardinal points or directions of north, south, east, and west.>>
 Milky Way Over Spains Bardenas Reales
Milky Way Over Spains Bardenas Reales